
LetsDefend has released a new DFIR challenge called “REvil Ransomware.” Let’s walk through this investigation together and answer questions for this challenge!
Attempt the challenge on your own first! If you get stuck, then refer to the guide. If you finished the challenge, comparing your analysis process to the one in this guide may help you improve.
The challenge instructions are: “We have extracted the memory dump from the compromised machine. Find the evidence of the ransomware attack.”
So let’s start by downloading the memory dump zip file and unpacking it.
Before we continue, we need to read through the 10 questions we need to answer to solve this challenge. Make sure you keep the questions in mind while we do our analysis.
Investigation Prep-work
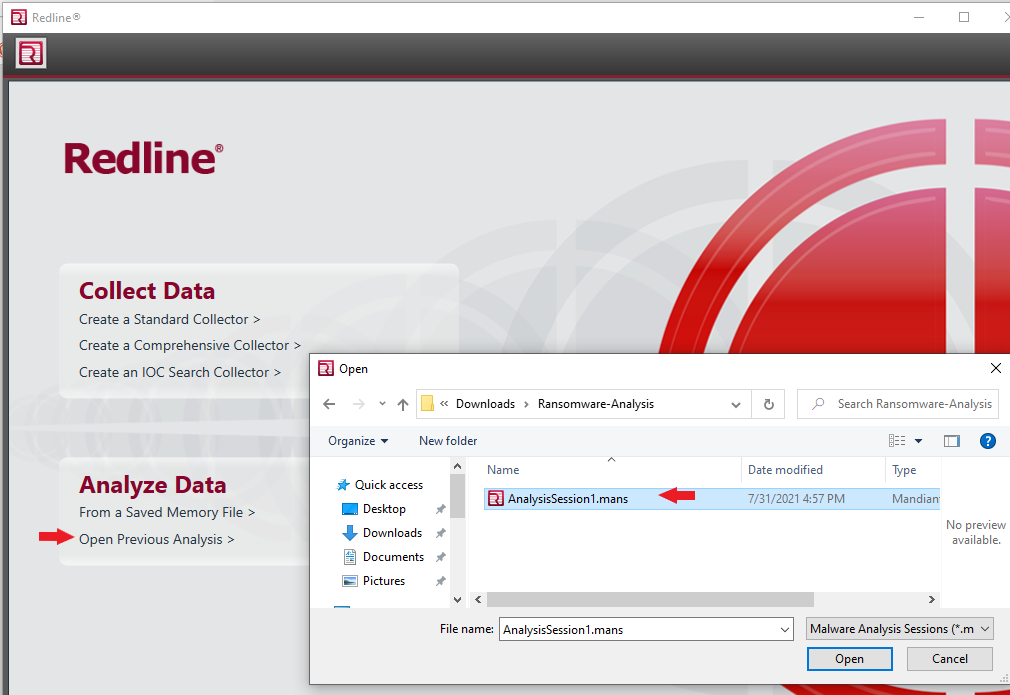
Before we can begin, we need to set up a tool called Redline produced by FireEye. Redline is a free tool that can gather system details and create a memory dump file of a system after an incident. Redline collects data about processes, temp memory, drivers, registry, and other crucial data to determine what happened in the breach. So we will need to download the tool and install it. I recommend setting up a VM(6x CPU, 8GB RAM, 64GB HDD, OS-Win10) to do all this work, but that is optional. Download and install the tool, then continue.
URL: https://fireeye.market/apps/211364Redline Data Analysis
After installing the Redline tool, download and extract the LetsDefend “Memory Dump” file. Open Redline and open the now extracted “AnalysisSession1.mans” file.
Get to Know the System
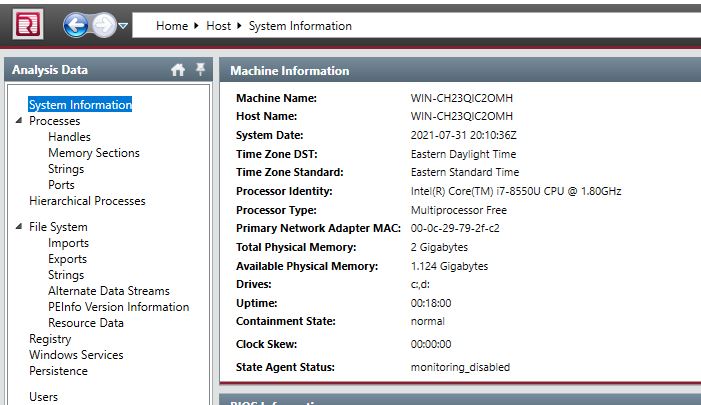
It would be best if you started every investigation by getting to know the system you are investigating. For example, the Operating System, the User who uses the system, what the system is used for, etc. Information like this is critical because investigating an infection on an end-user computer is a different process than, for example, an IIS web server.
Start by clicking on the “System Information” section in the left-hand navigation bar. From here, we can answer questions number 1 & 2.
Ransomware as a Service
Ransomware attacks are a business. Like most businesses, not everything is done in-house. The person who breaks into a network, a Threat Actor, is not the same person who writes the malware that locks files. The Threat Actor can outsource the ransom malware part to a third party; this is Ransomware as a Service(RaaS). In this model, the Threat Actor only needs to focus on what he is good at, breaching networks. The rest of the process is outsourced to the RaaS gang, who split the profits when the ransom is collected.
Ransome Note
We can save time with our investigation by looking up the gang’s tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTP). We can search with the ransom note to identify the gang behind the malware. Ransom notes are unique to each gang or malware, and we will identify the group with some online searches. The ransom note is intentionally left where we can find it, making this easy to find.
In the case of this challenge, the ransom note was included in the zip file. So open up the ransom note and read through it. From here, we can answer questions number 6 & 7.
---=== Welcome. Again. ===---
[-] Whats HapPen? [-]
Your files are encrypted, and currently unavailable. You can check it: all files on your system has extension 993ixjlb.
By the way, everything is possible to recover (restore), but you need to follow our instructions. Otherwise, you cant return your data (NEVER).
[+] What guarantees? [+]
Its just a business. We absolutely do not care about you and your deals, except getting benefits. If we do not do our work and liabilities - nobody will not cooperate with us. Its not in our interests.
To check the ability of returning files, You should go to our website. There you can decrypt one file for free. That is our guarantee.
If you will not cooperate with our service - for us, its does not matter. But you will lose your time and data, cause just we have the private key. In practice - time is much more valuable than money.
[+] How to get access on website? [+]
You have two ways:
1) [Recommended] Using a TOR browser!
a) Download and install TOR browser from this site: https://torproject.org/
b) Open our website: http://aplebzu47wgazapdqks6vrcv6zcnjppkbxbr6wketf56nf6aq2nmyoyd.onion/4FE49B3286F992CB
2) If TOR blocked in your country, try to use VPN! But you can use our secondary website. For this:
a) Open your any browser (Chrome, Firefox, Opera, IE, Edge)
b) Open our secondary website: http://decoder.re/4FE49B3286F992CB
Warning: secondary website can be blocked, thats why first variant much better and more available.
When you open our website, put the following data in the input form:
Key:
cmWRTrhGaxBPY61xDVvWNmN3BNqoc69oKOOyT9szKN0MkbLuWDglAjdvXpRtM04o
U6CwlksW972OjnRNPyLxsrdgQ6vKLBgNVU9EeBdNKIe0xx00W+f52FjzBHSU6Uqj
jA9+x4nQlb1UnBfh03fudODALR0OwOEPLJRA6UwVgBU5sTIxSS2XeDW54xQiIaQ2
2LwacPyp6uB9KG9HzuOrYaoGF2dkck5vztvYs7x5/PdniIsVeKWJT18lxS+pvr5H
iOnmvbb15EzVHWXoX3QLOrzlXwVyN3SObOi6wxgbavBvmL5nkhum7omuV2pijbDB
Zql60QG+f/0AvJ9c+Mv6FqfBP7bAaPAJbMyM/Azl800yhIlTVKptuHj6yLTaSf08
k9N21UjIgvVFPaXnkiuK+1tV9lPNhc86JzqXyPvaW91Qs+brytctNuxNX9u5aDCP
Hl9hq0352ViUNQel60jHZjZxMPmiqcvMKh7f5xpVQWANm7CNqL8/orfZdSSwUfmG
3Vybt4yx7/J9tG74ljaZZFZjEW6vX6ZhGR93zjH8f4ocJe3rhfxCsMPW/ClxQbU4
sTekXfCxRLye8ryr1D7aPI5tSnadE5IhVQHNyub2NdlDypjwV5RIsds2b1PGCN/R
s/T9s5A18bkKhhItchGS37N1VcK4tJY9HMNwYMtOu7yevZjvS9NYAQT/p7eceSvp
4e2gej7F6wx8BDsORCapTTeKfy/wqr9PE0PtwVc0bICU8404QnEMPR4ENMfTFVD1
C859u1JvmxXdCvutFSomZaEvVZGuT7ZELqllCbPbHaBFslOxylmOrb4yKHkANN0i
tHrccO/ntE/db6l0zmh/wbBdUusMn/+MeljdDAdzJUon4VHBme9ew52E8EwwjDxr
gMDwV0VaBarxY+cOlvzhi/y6hAhrUHc0pN/qQmJdIk+vVLyAvnAq4kvS+TCr9J/9
Cf6HJ0anEFnArXyEch/Yj++o4Zur+sJBiNOZzCUZuHtMZSor2eIU2w0uYfYb8Yt7
E10KLssTcTJuXs52JYEMU+TFpjJkMl0GHjpfmSoz68hQhKlHQyzLbiT9KwRi86Iz
sRA9qkotYREsA5xMDgK6OE3K97n7/+MUOlpZcP49Q7mrN9oQnnSnRAcstk3mWy4I
Stjb1E0uYGTHiBxp9KR6hCMwnAlrnWZjSDV+iyvfxvq7+Ao6SiCHRBA5JTrAco2G
aqntlqVZ0MuqLTsl8LkH8ND7lHz7xkOsv1q9phL+tfNvUikXyBpJwxTbm6QWKDNM
va/odyk4MHOqz3SvCd+pxMsUdJyoxtAvC08inXiFUL8SQyVkUfSXdhRm0Jy/hZxj
LAKStSCWL/8=
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
!!! DANGER !!!
DON'T try to change files by yourself, DON'T use any third party software for restoring your data or antivirus solutions - its may entail damage of the private key and, as result, The Loss all data.
!!! !!! !!!
ONE MORE TIME: Its in your interests to get your files back. From our side, we (the best specialists) make everything for restoring, but please should not interfere.
!!! !!! !!!We can use an online tool “ID Ransomware” to determine the ransomware gang.
URL: https://id-ransomware.malwarehunterteam.comUploading the ransom note to the site will identify the gang behind the malware.
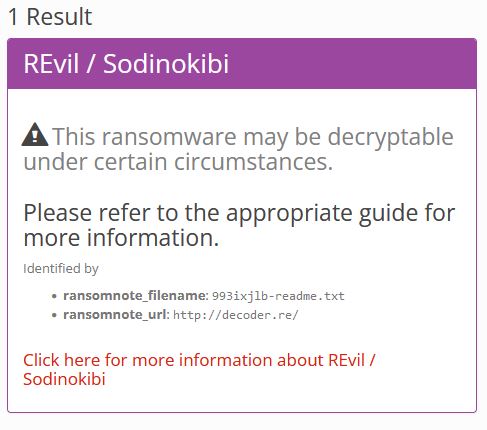
We can answer question number 10!
Other Methods of Identifying Ransom Notes
- Get the ransom note file hash and search VirusTotal.
- Search key phrases from the note in Google.
Looking For The Malware
We need to work the infection process backward to find the malware and its infection methodology. Let’s look through the file creation timeline to discover what files were created leading up to the infection.
- Open the “File System” menu from the left-hand navbar.
- Click the checkbox “C:\”. This will cause all files on the drive to be shown.
- Click the “Created” column till it sorts the file with the newest to oldest creation timestamp.
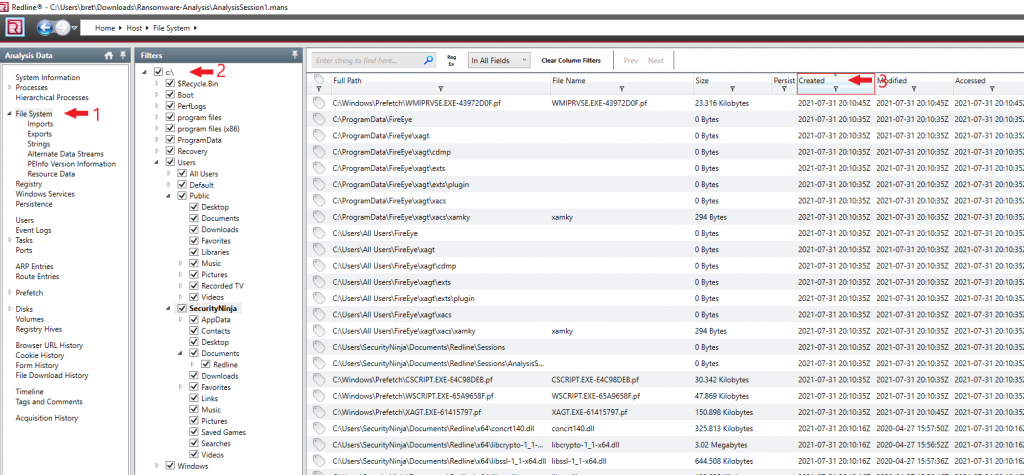
The last known thing done on the system was installing the Redline collection tool, so those files should be at the top of the list. Just after the Redline tool install is where we want to look for signs of malware. Review the list for files that stand out, like executables or scripts.
File History Events
Looking through the file history, we find the following series of events.
- Install Redline.
- Prefetch files were created for a few executables, suggesting they were run.
- ReadMe ransom notes were created.
- Sample documents are encrypted by the malware.
- 7-Zip installed.
- Firefox installed.
We can find the malware in the file history just before the encryption process. The malware is within the Downloads folder, so it may have been downloaded with a web browser. Open the “File Download history” section from the left-hand menu. It’s pretty clear from the download history which file contains the malware.
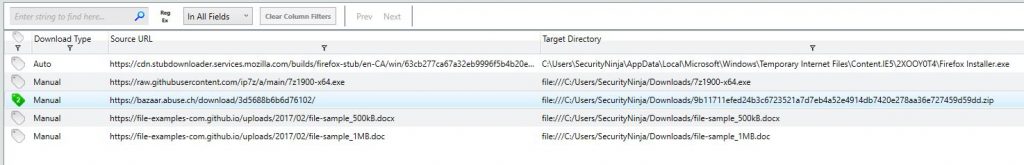
So we now know the malware and how it got on the system. However, this forensic image has told us everything it can.
Malware Analysis
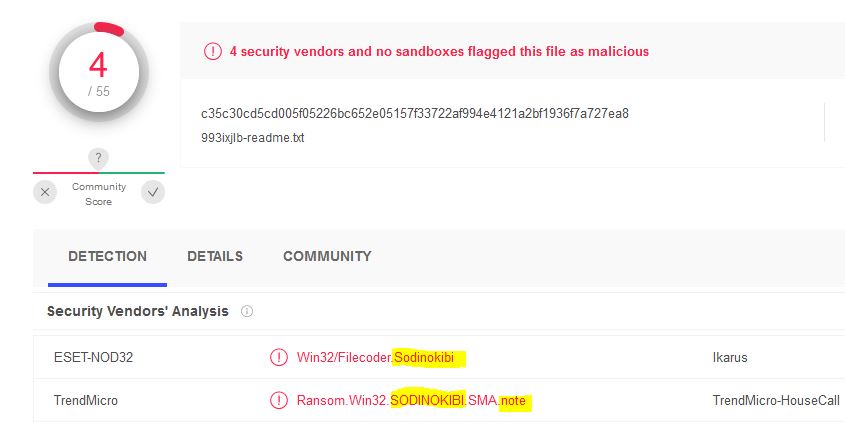
Now that we have a file hash of the malware discovered in the Downloads folder, we can consult a few online resources.
Virus Total
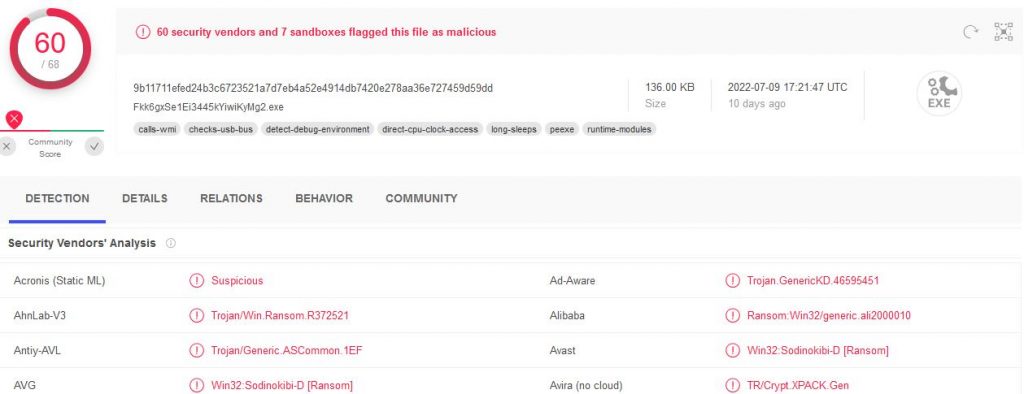
Encase we were still unclear, Virus Total confirms we found the malware.
Joe Sandbox Analysis
We can get a dynamic malware analysis report from a few online tools. Joe Sandbox Analysis will have historical reports that we can search for more details on this malware. Go to the following URL and search with the malware hash we found earlier.
URL: https://www.joesandbox.com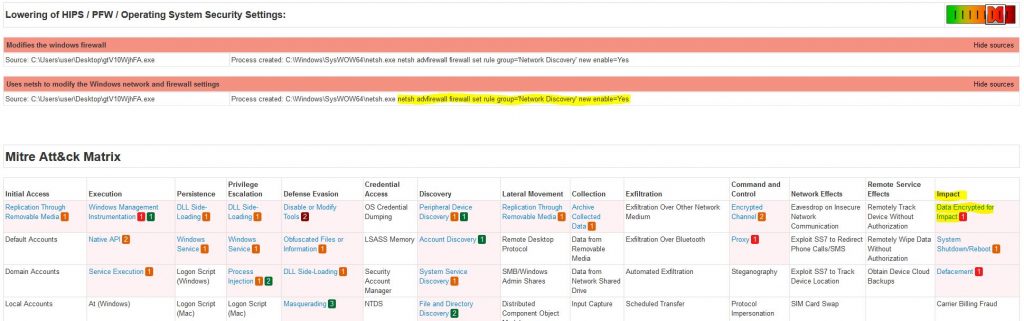
Within the malware report, we can find the missing details about the malware that we need to answer the remaining questions 8 & 9.
Incident Response Postmortem
This DFIR comes from a simulated event, but let’s treat this as if this was a real event. What have we learned from this incident, and how can we protect ourselves in the future?
What were the security gaps, and how can we fix them?
- A user account was able to download and run malware.
– This could have been stopped if the “SecurityNinja” account was not in the “Administrators” group. Creating a separate User and Administrator account will prevent any process from running privileged tasks without express permission. - Anti-Virus did not detect the malware.
– An up-to-date AV would have caught this malware and stopped it. Even when I copied the raw text of the ransom note, my forensics system’s AV started alerting; not the malware, just the ransom notes text! - Running an outdated Operating System.
– This is a common thread in most malware infections today. Windows 7, and Server 08(R2) are very insecure by today’s standards. - The user account “SecurityNinja” is compromised, or the owner of the “SecurityNinja” account is a malicious insider.
– If the “SecurityNinja” account was compromised, we need to investigate further how that happened.











Leave a Reply